CO2 refrigeration / co2 cold room manufacture / co2 cold room supplier
Brief for "CO2 refrigeration"
What's the goal of the piece?
The goal of this piece is to provide an in-depth analysis of the use of CO2 as a refrigerant, focusing on its environmental benefits and the challenges associated with its low critical temperature and high operating pressure. The article will also explore recent advancements in reducing energy consumption in CO2 refrigeration cycles, making it a valuable resource for industry professionals and researchers.
www.manacoldroom.com
Who is it for?
This piece is targeted at HVAC professionals, environmental engineers, researchers in refrigeration technology, and sustainability advocates who are interested in the latest developments in eco-friendly refrigerants.
How long should it be?
The article should be approximately 2,000 to 2,500 words to cover the topic comprehensively while maintaining reader engagement.
What's the value prop?
The article offers valuable insights into the use of CO2 as a refrigerant, including its environmental benefits and the latest technological advancements to improve its efficiency. Readers will gain a deeper understanding of how CO2 can be optimized for commercial refrigeration, making it a viable alternative to high-GWP refrigerants.
What's the CTA?
Encourage readers to subscribe to the newsletter for updates on the latest research and advancements in refrigeration technology. Additionally, prompt them to download a detailed whitepaper on CO2 refrigeration cycles for more technical insights.
Outline
Introduction
- Brief overview of CO2 as a refrigerant
- Importance of eco-friendly refrigerants due to high-GWP restrictions
The Environmental Benefits of CO2 as a Refrigerant
- Explanation of CO2's low GWP
- Comparison with traditional refrigerants
Challenges of Using CO2 in Refrigeration
- Low critical temperature
- High operating pressure
- Energy consumption concerns
Recent Advancements in CO2 Refrigeration Technology
- Overview of transcritical CO2 refrigeration cycles
- Thermodynamic analysis and pressure optimizations
Case Studies: Transcritical CO2 Refrigeration Cycles
- Booster cycle
- Parallel compression cycle
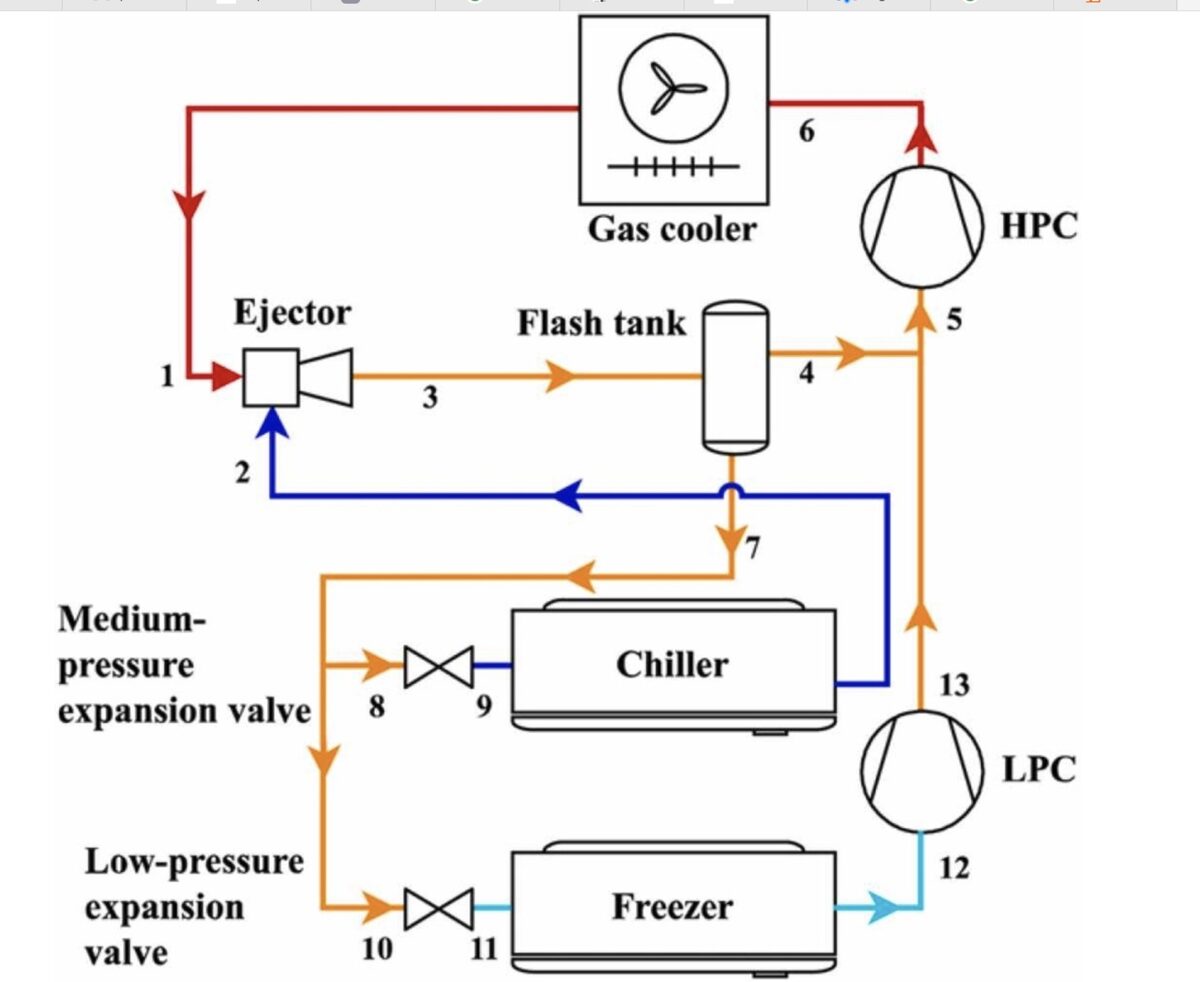
- Ejector expansion cycle
Performance Comparison of Different CO2 Cycles
- Analysis of Coefficient of Performance (COP)
- Impact of different operational conditions
Future Prospects and Research Directions
- Potential for further energy consumption reduction
- Emerging technologies and innovations
Conclusion
- Summary of key points
- Reiteration of CO2's potential as a sustainable refrigerant
Call to Action
- Subscribe to the newsletter
- Download the whitepaper
List of Keywords to Include Throughout the Content
- CO2 gas
- Carbon dioxide refrigerant
- Transcritical CO2 refrigeration
- High-GWP refrigerants
- Eco-friendly refrigerants
- CO2 refrigeration cycles
- Energy consumption in refrigeration
- Thermodynamic analysis
- Pressure optimization
- Coefficient of Performance (COP)
- Ejector expansion cycle
- Commercial refrigeration
- Sustainable refrigerants
- HVAC industry
- Environmental benefits of CO2